WordPress is the most popular Content Management System (CMS) in use today. According to its Wikipedia page, WordPress is used by more than 23.3% of the top 10 million websites as of January 2015.
This popularity also makes WordPress a target for hackers. If you’re running WordPress, have you ever looked at the Web server logs? Look at all the attempts to access wp-login.php (the login page). Hint: the vast majority of them are not you. Same with xmlrpc.php. Do you need XML-RPC for your WordPress installation? Probably not.
Assuming your WordPress site is on Linux/Apache/MySQL, there are some things you can do to secure it. If you don’t have access to make changes to .htaccess files and/or if AllowOverride is not enabled for your site, contact your System Administrator.
- First, always make sure you stay current with WordPress Platform and Plug-In updates.
- Use Apache .htaccess to block access to the wp-login.php and xmlrpc.php to everyone except yourself. If your static IP is 192.168.50.10, you would add this to the .htaccess file in the root of your Web directory:
- Use Apache .htaccess to block access to the entire wp-admin directory to everyone except yourself. If your static IP is 192.168.50.10, you would add this to the .htaccess file in the root of the wp-admin directory:
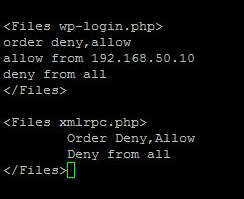
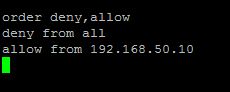
Bots (and people) who attempt to access your WordPress login page or anything in the Admin directory will get a 403 Forbidden error message. These would-be attackers will be denied and will move on to attack some other site instead.

If you have a WordPress site, contact us for help to secure it.